My broadband speed is slower than advertised
The UK Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) enforces strict guidelines on how internet service providers (ISPs) can advertise broadband speeds. An ISP must display the average speed that at least 50% of their customers can achieve during peak hours (8pm-10pm).
For example, a standard ADSL broadband package from TalkTalk may offer a maximum speed of 17Mbps, but it can only advertise the package at 11Mbps, which represents the average speed customers can expect during peak hours. All broadband deals listed on FasterBroadband.co.uk are displayed with the peak average customer speed. To view the maximum achievable speed for any deal, click on its key features link on our Broadband Deals page.
When switching broadband providers, your new ISP should clearly state the speed you are likely to achieve at your property. This may differ from the advertised average speed. However, they must specify your minimum guaranteed speed before you agree to the contract.
Right to exit (RTE) process
Not all ISPs have signed up for this voluntary Ofcom code of practice. If your provider has, and your broadband speed falls below the agreed minimum, you have the right to exit your contract without incurring early termination fees, provided the issue is not resolved within 30 days of reporting the fault. This right to exit also applies to bundled TV services on the same line, regardless of whether these services were purchased together or under the same contract. Please note that within the 30-day period, you must reasonably accommodate any engineer visits deemed necessary. If you fail to make yourself available when required, the 30-day period will be extended accordingly. A copy of Ofcom's current RTE process can be viewed here: Ofcom Voluntary Code of Practice (Residential) PDF
Currently, the following residential ISP's have joined this Ofcom code of practice:
- BT (BT broadband reviews)
- EE (EE broadband reviews)
- Hyperoptic
- Now Broadband (Now broadband reviews)
- Plusnet (Plusnet broadband reviews)
- Sky (Sky broadband reviews)
- TalkTalk (TalkTalk broadband reviews)
- Utility Warehouse
- Virgin Media (Virgin broadband reviews)
- Zen (Zen broadband reviews)
What is a good internet speed for streaming TV?
You should be able to stream TV programmes comfortably with a connection speed as low as 3Mbps. For example, streaming BBC iPlayer programmes in Standard Definition (SD) requires a connection speed of 1.5Mbps. However, if you choose to stream in High Definition (HD), a connection speed of 5Mbps is required. If you experience buffering problems with streaming in HD, switching to SD should resolve this.
| TV Service | SD Standard definition | HD High definition | 4K Ultra HD |
|---|---|---|---|
| BBC iPlayer | 1.5Mbps | 5Mbps | Not available |
| Netflix | 3Mbps | 5Mbps | 25Mbps |
| Now TV | 2.5Mbps | Not available | Not available |
| YouTube | 1.1Mbps | 5Mbps | 20Mbps |
| Apple TV | 2.5Mbps | 8Mbps | 25Mbps |
Apple MAC WiFi diagnostics tool
macOS includes a built-in WiFi diagnostics tool that is often overlooked. This is not surprising, as it is somewhat hidden, but it remains an excellent way to monitor your WiFi signal strength. Follow the steps below to begin tracking your WiFi signal in real time.
Step 1: Hold down the Option (Alt) ⌥ key (to the left of the space bar), whilst clicking the WiFi icon in the top right of your screen.
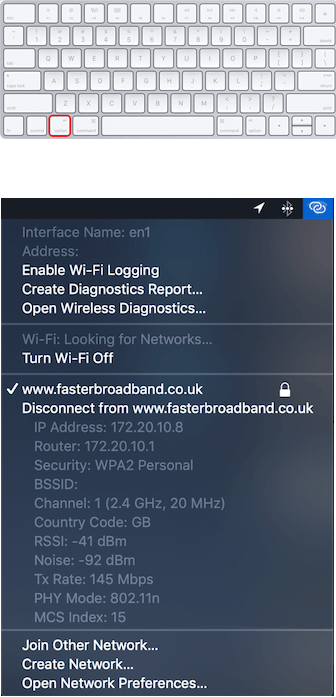
Step 2: You should now see a dropdown menu, similar to the one pictured below. The contents of this menu are useful, as they display the type of WiFi network you're connected to. It also shows the frequency band your router is transmitting on (see Channel)—either the 2.4 GHz or the faster 5 GHz range. Ideally, the security type should be WPA2, or the more recent WPA3. If the security is listed as WEP or WPA (without any numbers following it), the security of your network traffic is compromised.
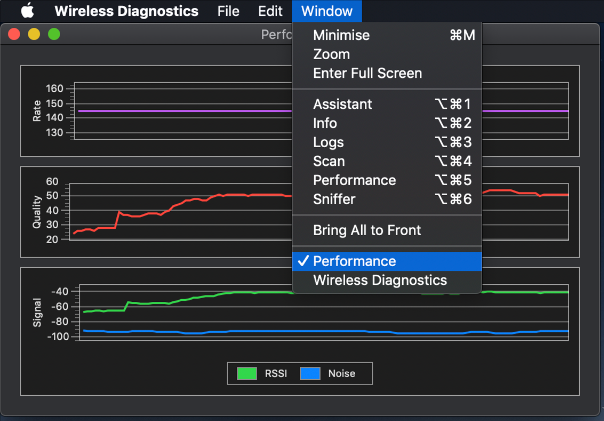
Step 3: In the dropdown menu, select Open Wireless Diagnostics. Once the program window opens, navigate to the menu tab and select Performance, as shown in the image above.
Step 4: The program will display three live performance graphs, providing information you can use to diagnose faults, compare different routers, or test different router positions.
The macOS WiFi diagnostics tool uses live graphs to display the following key aspects of your WiFi connection:
Rate: Shows the WiFi transmission rate over time, measured in megabits per second.
Quality: Displays the signal-to-noise ratio over time. If the quality is too low, your device will disconnect from the WiFi router. Several factors can affect your WiFi signal quality, including the distance between your device and the router, obstruction from objects like walls, and interference from other electrical items such as microwave ovens, WiFi printers, and cordless phones.
Signal: Displays both the signal (RSSI) and noise measurements over time. For optimal performance, you want the RSSI to be high and the noise to be low. The larger the gap between the RSSI and the noise, the better.